File:PMC4491724 emm201532f4.png
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
PMC4491724_emm201532f4.png (512 × 512 pixels, file size: 172 KB, MIME type: image/png)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
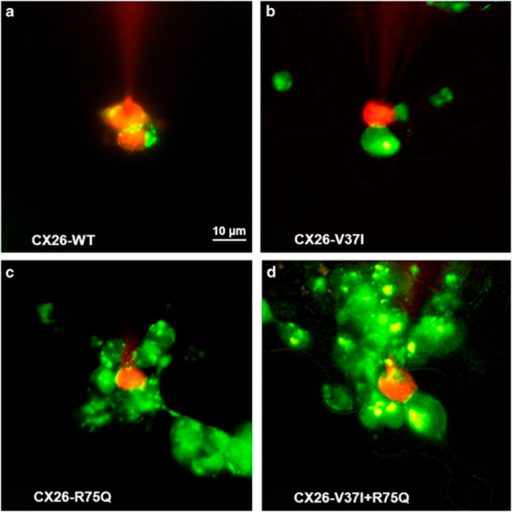
| current | 19:58, 23 January 2022 |  | 512 × 512 (172 KB) | Ozzie10aaaa | Author:Kim J, Jung J, Lee MG, Choi JY, Lee KA ,Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine(Openi/National Library of Medicine)Source:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC4491724_emm201532f4&query=&req=4 Description:fig4: Biochemical coupling through (a) Cx26-WT and (b–d) mutant gap junctions. The intercellular dye transfer using propidium iodide (PI) was conducted. It is of note that, in cells expressing wild-type gap junctions, dye readily travel... |
File usage
The following page uses this file: