This file is from a shared repository and may be used by other projects.
The description on its file description page there is shown below.
License
Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Summary
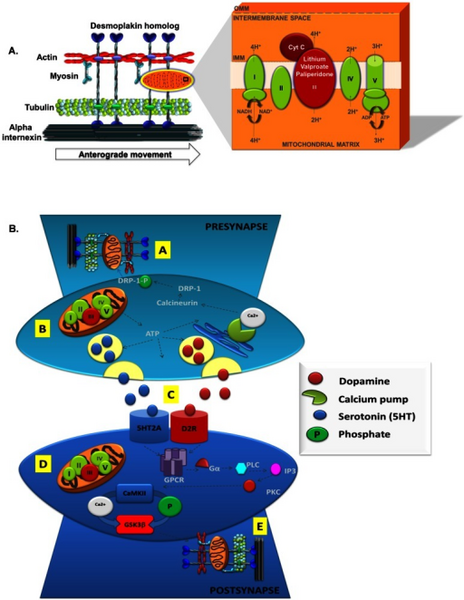
Author:Corena-McLeod M, Walss-Bass C, Oliveros A, Gordillo Villegas A, Ceballos C, Charlesworth CM, Madden B, Linser PJ, Van Ekeris L, Smith K, Richelson E,Neuropsycopharmacology Laboratory, Mayo Clinic (Openi/National Library of Medicine) Sources:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC3653908_pone.0052147.g004&query=Paliperidone&it=xg&req=4&npos=3 Description:pone-0052147-g004: Simplified scheme to illustrate the effects of lithium, valproate and paliperidone treatment on mitochondrial and cytoskeletal protein phosphorylation with effects on mitochondrial transport towards the synapse.A. Cytoskeletal proteins (desmoplakin homolog, myosin, actin, tubulin and alpha internexin) are phosphorylated and involved in the mechanism of anterograde mitochondrial transport. Actin fiber formation is promoted by phosphorylation of actin isoforms. Actin binding domains indicated as purple ovals contribute to network formation through binding of desmoplakin homolog to actin. Phosphorylation of tubulin isoforms promotes microtubule formation and binding to desmoplakin homolog is facilitated through tubulin binding domains (green ovals). Tubulin in turn binds alpha internexin. Anterograde mitochondrial movement is possible through Myosin interaction with actin. Inside the mitochondria (insert), UQCRC1 from complex III (red) was phosphorylated after treatment with all three drugs with effects on mitochondrial function. B. Schematic representation of the effects of anterograde mitochondrial movement on synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission. Each step where the drugs have effects is indicated by a yellow square and a letter inside. These events may or may not happen simultaneously. A. Anterograde mitochondrial movement to the pre-synapse is promoted by all three drugs. B. Mitochondrial function near SNARE complexes provides necessary ATP for neurotransmitter release as well as regulation of Ca2+ levels. Myosin heavy chain also plays a role on synaptic vesicle opening. Ca2+ affects calcineurin which in turns affects DRP-1. Phosphorylation of DRP-1 influences mitochondria. C. Serotonin and dopamine release is regulated by 5HT2A and D2 receptors. The ratio of serotonin (5HT) and dopamine (DA) available regulates mitochondrial movement to the post-synapse as serotonin promotes anterograde movement while dopamine inhibits it. D. Mitochondrial function at post-synaptic terminals contributes to Ca2+ homeostasis influencing CAMKII and GSK3β E. Mitochondrial transport to the post-synapse results in increased levels of ATP necessary for proper functioning of post-synaptic machinery. The number of mitochondria is directly and reciprocally related to the number of active synapses (Li et al., 2004).
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment |
|---|
| current | 19:46, 2 February 2022 |  | 512 × 662 (310 KB) | Ozzie10aaaa | Author:Corena-McLeod M, Walss-Bass C, Oliveros A, Gordillo Villegas A, Ceballos C, Charlesworth CM, Madden B, Linser PJ, Van Ekeris L, Smith K, Richelson E,Neuropsycopharmacology Laboratory, Mayo Clinic (Openi/National Library of Medicine) Sources:https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult?img=PMC3653908_pone.0052147.g004&query=Paliperidone&it=xg&req=4&npos=3 Description:pone-0052147-g004: Simplified scheme to illustrate the effects of lithium, valproate and paliperidone treatment on mitochondr... |
File usage
The following page uses this file: