File:Cross-reactivity hypothesis for the onset of dermatitis herpetiformis in patients with celiac disease.tif
From WikiProjectMed
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

Size of this PNG preview of this TIF file: 800 × 380 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 152 pixels | 640 × 304 pixels | 1,024 × 486 pixels | 1,962 × 931 pixels.
Original file (1,962 × 931 pixels, file size: 442 KB, MIME type: image/tiff)
This file is from a shared repository and may be used by other projects. The description on its file description page there is shown below.
Summary
| DescriptionCross-reactivity hypothesis for the onset of dermatitis herpetiformis in patients with celiac disease.tif |
English: Gliadin proteins in gluten are absorbed by the gut and enter the lamina propria where they need to be deamidated by tissue transglutanimase (tTG). tTG modifies gliadin into a more immunogenic peptide. Classical dendritic cells (cDCs) endocytose the immunogenic peptide and if their pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are stimulated by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMPs), the danger signal will influence them to secrete IL-8 (CXCL8) in the lamina propria, recruiting neutrophils. Neutrophil recruitment results in a very rapid onset of inflammation. Therefore, co-infection with microbes that carry PAMPs may be necessary for the initial onset of symptoms in gluten sensitivity, but would not be necessary for successive encounters with gluten due to the production of memory B and T cells (discussed below). In celiac disease, tTG is treated as an autoantigen, especially in people with certain HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 alleles and other gene variants that cause atopy. tTG is up-regulated after gluten absorption. cDCs endocytose tTG-modified gliadin complexes or modified gliadin alone but they only present gliadin to CD4+ T cells on pMHC-II complexes. These T cells become activated and polarised into type I helper T (Th1) cells. Th1 cells against gliadin have been discovered, but none against tTG. A naive B cell sequesters tTG-modified gliadin complexes from the surface of cDCs in the lymph nodes (LNs) before they become endocytosed by the cDCs. The B cell receptor (membrane bound antibody; BCR) is specific to the tTG portion of the complex. The B cell endocytoses the complex and presents the modified gliadin to the activated Th1 cell's T cell receptor (TCR) via pMHC-II. Thus, the B cell presents the foreign peptide (modified gliadin) but produces antibodies specific for the self-antigen (tTG). Once the B cell becomes activated, it differentiates into plasma cells that secrete autoantibodies against tTG, which may be cross-reactive with epidermal transglutanimase (eTG). Class A antibodies (IgA) deposit in the gut. Some may bind to the CD89 (FcaRI) receptor on macrophages (M1) via their Fc region (constant region). This will trigger endocytosis of the tTG-IgA complex, resulting in the activation of macrophages. Macrophages secrete more IL-8, propagating the neutrophil-mediated inflammatory response. In dermatitis herpetiformis, the purportedly cross-reactive autoantibodies may migrate to the skin. IgA deposits may form if the antibodies cross-react with epidermal transglutanimase (eTG). Macrophages may be stimulated to secrete IL-8 by the same process as is seen in the gut, causing neutrophils to accumulate at sites of high eTG concentrations in the dermal papillae of the skin. Neutrophils produce puss in the dermal papillae, generating characteristic blisters. IL-31 accumulation at the blisters may intensify itching sensations. Memory B and T cells may become activated in the absence of PAMPs and DAMPs during successive encounters with tTG-modified gliadin complexes or modified gliadin alone, respectively. Symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis are often resolved if patients avoid a gluten-rich diet. |
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | LBNBM OBIBT |
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license:
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible license as the original.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
some value
17 November 2017
image/tiff
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:53, 17 November 2017 | 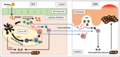 | 1,962 × 931 (442 KB) | commons>LBNBM OBIBT | User created page with UploadWizard |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Width | 1,962 px |
|---|---|
| Height | 931 px |
| Compression scheme | LZW |
| Pixel composition | RGB |
| Number of components | 4 |
| Number of rows per strip | 1 |
| Horizontal resolution | 150 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 150 dpi |
| Data arrangement | chunky format |