Angiofibroma
| Angiofibroma | |
|---|---|
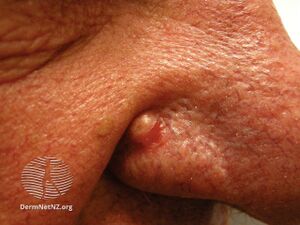 | |
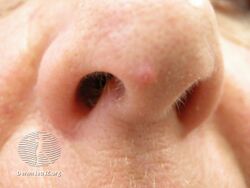
| Angiofibroma of the nose | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | One or many small bumps in skin[1] |
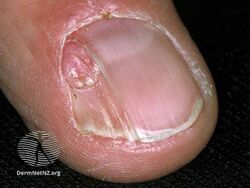
| Types | Multiple fibrous papules of the face, pearly penile papules, fibrous papule of the nose, periungal angiofibroma,[1] acral fibrokeratoma,[2] |
| Causes | Local overgrowth of fibroblasts, collagen and blood vessels[3] |
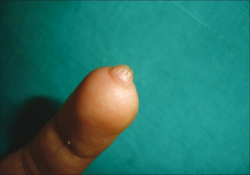
Angiofibroma is a small bump in the skin classified by where in the body it appears or by its association with a genetic condition.[1][3] There may be one or many.[4] Acquired types include pearly penile papules, fibrous papules of the face and acral fibrokeratoma,[2] which includes angiofibromas under the nail and those at the fingertip.[5] Angiofibroma may be associated with tuberous sclerosis, Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1.[2]
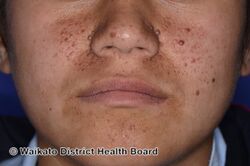
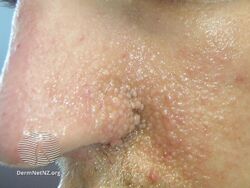
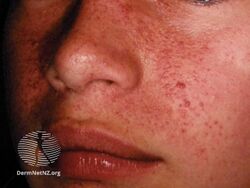
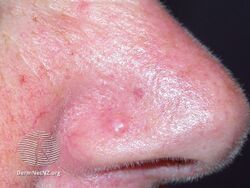
Angiofibromas are caused by a local overgrowth of blood vessels, collagen and fibroblasts.[3] The angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis usually appear in childhood, are small, yellow-brown or flesh-colored, smooth, shiny, 0.1 to 0.3 cm bumps present over the sides of the nose and the cheeks, in a butterfly distribution.[5][3] Later, oral fibroma or a periungal angiofibroma may appear.[3] A solitary fibrous papule typically occurring on the nose in an adult, and pearly penile papules are acquired angiofibromas.[3] Angiofibromas may be itchy, bleed and cause disfigurement.[3]
Diagnosis is by visualisation and biopsy.[3] Facial angiofibromas may appear similar to acne, basal cell carcinoma or intradermal nevus.[3] Viral warts and subungal exostosis can appear like angiofibromas in the nail.[3] Pearly penile papules can mimic molluscum contagiosum and genital warts.[3] Treatment is not always necessary.[3] Some options include excision, dermabrasion, lasers, electrical and radiofrequency procedures, cryotherapy, topical podophyllotoxin, topical rapamycin, or topical beta-blocker.[3]
Images
-
Angiofibromas face (butterfly distribution)
-
Angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis
-
Angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis
-
Fibrous papule of the nose
-
Fibrous papule of the nose
-
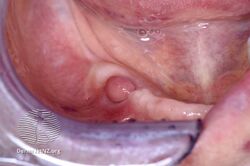
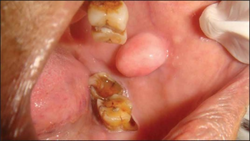
Angiofibroma in mouth
-
Angiofibroma inside cheek
-
Angiofibroma at fingertip (acquired fibrokeratoma)
-
Angiofibroma under nail
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Macri, Angela; Kwan, Eddie; Tanner, Laura S. (2021). "Cutaneous Angiofibroma". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 2023-04-27. Retrieved 2023-04-29.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "38. Vascular tumors". Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 709. ISBN 978-0-7020-6830-0. Archived from the original on 2021-05-25. Retrieved 2021-09-24.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 "Angiofibroma". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 13 August 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ↑ Paller, Amy S.; Mancini, Anthony J. (2020). "9. Cutaneous tumors and tumor syndromes". Clinical Pediatric Dermatology: A Textbook of Skin Disorders of Childhood and Adolescence (6th ed.). St Louis, Missouri: Elsevier. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-323-54988-2. Archived from the original on 2023-04-29. Retrieved 2023-04-29.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Johnstone, Ronald B. (2017). "34. Fibrous tumors and tumor-like proliferations". Weedon's Skin Pathology Essentials (2nd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 613–616. ISBN 978-0-7020-6830-0. Archived from the original on 2021-05-25. Retrieved 2021-09-24.
External links
| Classification |
|---|