Epiglottitis
| Epiglottitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Acute supraglottitis | |
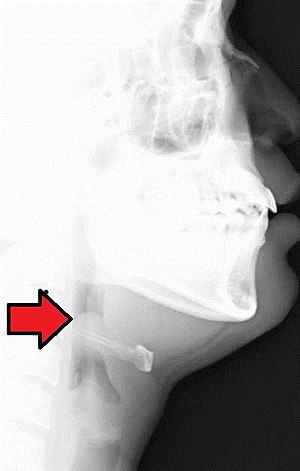 | |
| Neck X-ray showing thumbprint sign. | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
| Symptoms | Trouble swallowing, drooling, changes to the voice, fever, increased breathing rate, stridor[1][2] |
| Usual onset | Rapid[1][2] |
| Causes | H. influenzae type b, burns, trauma to the area[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging, looking at the epiglottis[3][1] |
| Prevention | Hib vaccine, rifampin[4][5] |
| Treatment | Endotracheal intubation, intravenous antibiotics, corticosteroids[1][2][4] |
| Prognosis | ~4% risk of death[3] |
| Frequency | ~2 per 100,000 per year[1][6] |
Epiglottitis is inflammation of the epiglottis—the flap at the base of the tongue that prevents food entering the trachea (windpipe).[7] Symptoms are usually rapid in onset and include trouble swallowing which can result in drooling, changes to the voice, fever, and an increased breathing rate.[1][2] As the epiglottis is in the upper airway, swelling can interfere with breathing.[7] People may lean forward in an effort to open the airway.[1] As the condition worsens stridor and bluish skin may occur.[1]
Epiglottitis was historically mostly caused by infection by H. influenzae type b.[8] With vaccination it is now more often caused by other bacteria.[1] Other possible causes include burns and trauma to the area.[1] The most accurate way to make the diagnosis is to look directly at the epiglottis.[3] X-rays of the neck from the side may show a "thumbprint sign" but the lack of this sign does not mean the condition is absent.[1]
An effective vaccine, the Hib vaccine, has been available since the 1980s.[4] The antibiotic rifampicin may also be used to prevent the disease among those who have been exposed to the disease and are at high risk.[5] The most important part of treatment involves securing the airway, which is often done by endotracheal intubation.[1] Intravenous antibiotics such as ceftriaxone and possibly vancomycin or clindamycin is then given.[2][4] Corticosteroids are also typically used.[1] With appropriate treatment, the risk of death among children with the condition is about one percent and among adults is seven percent.[3]
With the use of the Hib vaccine, the number of cases of epiglottitis has decreased by more than 95%.[9] While historically young children were mostly affected, it is now more common among older children and adults.[4] In the United States it affects about 1.3 per 100,000 children a year.[1] In adults between 1 and 4 per 100,000 are affected a year.[6] It occurs more commonly in the developing world.[10] In children the risk of death is about 6%; however, if they are intubated early it is less than 1%.[5]
Signs and symptoms
Epiglottitis is associated with fever, throat pain, difficulty in swallowing, drooling, hoarseness of voice, and stridor.[11] Onset is typically over a day.[11] The throat itself may appear normal.[11]
Stridor is a sign of upper airways obstruction and is a surgical emergency; the child often appears acutely ill, anxious, and will often try keeping the head held forward and insist on sitting up in bed. [12]
Complications
Among the possible complications for this condition are:[13]
Cause
Epiglottitis is typically due to a bacterial infection of the epiglottis.[1] While it historically was most often caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B with immunization this is no longer the case.[1] Bacteria that are now typically involved are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, or Staphylococcus aureus.[1]
Other possible causes include burns and trauma to the area.[1] Epiglottitis has been linked to crack cocaine usage.[14] Graft versus host disease and lymphoproliferative disorder can also be a cause.[4]
Diagnosis
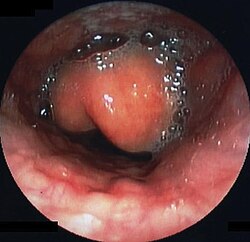
Diagnosis may be confirmed by direct inspection using a laryngoscope, although this may provoke airway spasm.[15] If epiglottitis is suspected, diagnosis is made on basis of fiberoptic laryngoscopy exam carried out in controlled environment like an operating room.[16][17]
-
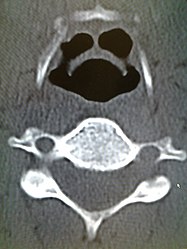
CT imaging showing the "halloween sign"
-
Left column: Normal epiglottis. Right column: Epiglottitis.
-
Swollen epiglottis in laryngoscopy
Imaging
On lateral C-spine X-ray, the thumbprint sign describes a swollen, enlarged epiglottis.[11] A normal X-ray, however does not exclude the diagnosis.[11] An ultrasound may be helpful if specific changes are present, but its use as of 2018 is in the early stages of study.[11]
CT imaging, is rarely needed and can have a negative effect via respiratory distress.[13]
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this condition indicates that other conditions such as peritonsillar abscess or retropharyngeal abscess which have similar clinical features should be ruled out.[13]
Prevention
An effective vaccine, the Hib vaccine, has been available since the 1980s.[4]
The antibiotic rifampicin may also be used to prevent the disease among those who have been exposed to the disease and are at high risk.[5]
Management
Airway management
The most important part of treatment involves securing the airway.[1] Epiglottitis may require urgent tracheal intubation to protect the airway.[1] Tracheal intubation can be difficult due to distorted anatomy and profuse secretions. Spontaneous respiration is ideally maintained until tracheal intubation is successful.[11] A surgical airway opening (cricothyrotomy) may be required if intubation is not possible.[11]
Medication
Intravenous antibiotics such as ceftriaxone and possibly vancomycin or clindamycin is then given[2][4], trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole or clindamycin may be an alternative.[18]Nebulized epinephrine may be useful to improve the situation temporarily.[11] Corticosteroids are also typically used.[1] Evidence for benefit however is poor.[11]
Prognosis
With appropriate treatment, the risk of death among children with the condition is about one percent and among adults is seven percent.[3] Some people may develop lymphadenopathy which could indicate a poor prognosis[13]
Epidemiology
While historically young children were mostly affected, it is now more common among older children and adults.[4] Before Hemophilus influenzae (Hib) immunization children of two to four were most commonly affected.[1] With immunization about 1.3 per 100,000 children are affected a year.[1]
Society and culture
Sarah Silverman spent a week in the ICU at Cedars Sinai Hospital with epiglottitis.[19][20]
George Washington is thought to have died of epiglottitis.[21] The treatments given to George Washington, such as severe bloodletting, an enema, vinegar, sage, molasses, butter, blistering his throat with Spanish fly, requiring him to swallow mercurous chloride and antimony potassium tartrate, and applying wheat poultices to various parts of the body, are no longer used.[22]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 Richards, AM (February 2016). "Pediatric Respiratory Emergencies". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 34 (1): 77–96. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2015.08.006. PMID 26614243.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Zoorob, R; Sidani, MA; Fremont, RD; Kihlberg, C (1 November 2012). "Antibiotic use in acute upper respiratory tract infections". American Family Physician. 86 (9): 817–22. PMID 23113461.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Westerhuis, B; Bietz, MG; Lindemann, J (August 2013). "Acute epiglottitis in adults: an under-recognized and life-threatening condition". South Dakota Medicine : The Journal of the South Dakota State Medical Association. 66 (8): 309–11, 313. PMID 24175495.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Schlossberg, David (2015). Clinical infectious disease (Second ed.). p. 202. ISBN 9781107038912. Archived from the original on 2016-08-16.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Blacklow, Neil R. (2004). Infectious diseases (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 461. ISBN 9780781733717. Archived from the original on 2016-08-16.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Textbook of Adult Emergency Medicine (4 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. 2014. p. 291. ISBN 9780702054389. Archived from the original on 15 August 2016. Retrieved 15 July 2016.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Hamborsky, j (2015). "Haemophilus influenzae type b". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (13 ed.). Public Health Foundation. p. Chapter 8. ISBN 9780990449119. Archived from the original on 20 July 2016. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- ↑ Yeh, Sylvia H. (2022). "4. Haemophilus influenzae Type B". In Jong, Elaine C.; Stevens, Dennis L. (eds.). Netter's Infectious Diseases (2nd ed.). Elsevier. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-323-71159-3. Archived from the original on 2022-12-15. Retrieved 2022-12-15.
- ↑ Des Jardins, Terry (2015). Clinical Manifestations & Assessment of Respiratory Disease (7 ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 529. ISBN 9780323358972. Archived from the original on 2016-08-15.
- ↑ Boons, Geert-Jan (2009). Carbohydrate-Based Vaccines and Immunotherapies. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. p. 1222. ISBN 9780470473276. Archived from the original on 2016-08-15.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 11.9 Gottlieb, M; Long, B; Koyfman, A (May 2018). "Clinical Mimics: An Emergency Medicine-Focused Review of Streptococcal Pharyngitis Mimics". The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 54 (5): 619–629. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2018.01.031. PMID 29523424.
- ↑ "Epiglottitis". nhs.uk. 18 October 2017. Archived from the original on 3 December 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Guerra, Amanda M.; Waseem, Muhammad (2020). "Epiglottitis". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 14 January 2021.
- ↑ Buttaro, Terry Mahan; Trybulski, JoAnn; Polgar-Bailey, Patricia; Sandberg-Cook, Joanne. Primary Care - E-Book: A Collaborative Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 406. ISBN 978-0-323-35521-6. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 8 January 2021.
- ↑ Mahon, Connie R.; Lehman, Donald C.; Manuselis, George (2014). Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 777. ISBN 978-0-323-29262-7. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ↑ "Epiglottitis Workup: Approach Considerations, Nasopharyngoscopy/Laryngoscopy, Radiography". emedicine.medscape.com. Archived from the original on 30 November 2020. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ↑ Tresley, Jonathan; Saraf-Lavi, Efrat; Kryvenko, Oleksandr; Sargi, Zoukaa (2015). "Epiglottic masses identified on CT imaging: A case report and review of the broad differential diagnosis". The Neuroradiology Journal. 28 (3): 347–353. doi:10.1177/1971400915594517. ISSN 1971-4009. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ↑ Bennett, John E.; Dolin, Raphael; Blaser, Martin J. (2014). Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 787. ISBN 978-0-323-26373-3. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 17 January 2021.
- ↑ "Comedian Sarah Silverman 'lucky to be alive' after surgery". apnews.com. 2016-07-07. Archived from the original on 11 August 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- ↑ "Sarah Silverman Says She Almost Died Last Week, Recounts Terrifying ICU Story". etonline.com. Archived from the original on 2 June 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- ↑ Henriques, Peter R. (2000). The Death of George Washington: He Died as He Lived. Mount Vernon, VA: Mount Vernon Ladies' Association. pp. 27–36. ISBN 978-0-931917-35-6.
- ↑ "Dec. 14, 1799: The excruciating final hours of President George Washington". PBS NewsHour. 2014-12-14. Archived from the original on 2017-12-27. Retrieved 31 December 2017.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Medscape Archived 2021-01-23 at the Wayback Machine