Enchondromatosis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Enchondromatosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Chondrodysplasia, skeletal enchondromatosis[1] | |
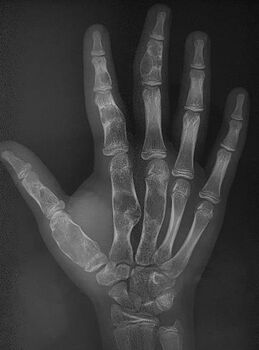
 | |
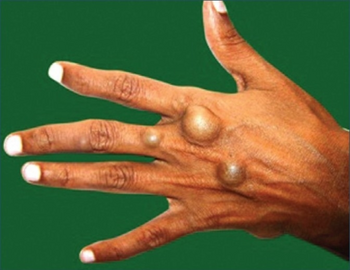
| Enchondromatosis in fingers | |
| Specialty | Orthopaedics[1] |
| Symptoms | Bone deformity, lump, broken bone[2] |
| Types | Ollier disease, Maffucci syndrome,metachondromatosis[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging.[1] |
| Prognosis | 40% risk of chondrosarcoma, increased risk of non-bone cancers[1] |
| Frequency | Rare[3] |
Enchondromatosis is the presence of multiple enchondromas, occurring as part of Ollier disease, Maffucci syndrome, or metachondromatosis.[3] It has a tendency to affect short tubular bones of the hands and feet, but can occur in long bones, shoulder blades and hips.[3] It presents with bone deformity, lumps, or broken bone, typically in a child.[2]
Diagnosis is by medical imaging.[1]
Enchondromatosis is rare.[3] 40% develop chondrosarcoma, and there is an increased risk of non-bone cancers such as gliomas and mesenchymal ovarian tumours.[1]
Images
-
Maffucci syndrome
-
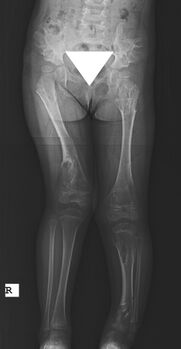
X-ray hips and legs: multiple enchondroma
-
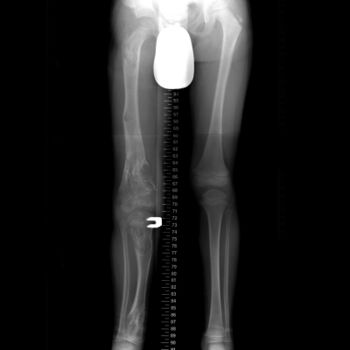
X-ray legs: Ollier disease
-
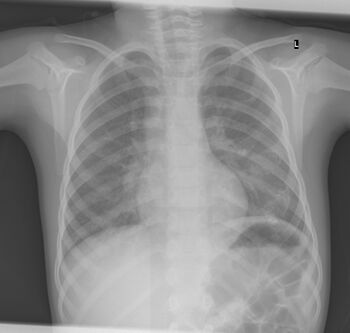
X-ray ribs: multiple enchondroma
-
X-ray wrist: Ollier disease in child
-
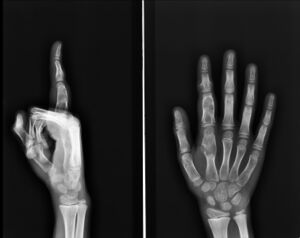
X-ray hand:Ollier disease in child
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Na, Kiyong; Park, Yong Koo (2020). "Multiple Enchondromatosis". In Santini-Araujo, Eduardo; Kalil, Ricardo K.; Bertoni, Franco; h, i (eds.). Tumors and Tumor-Like Lesions of Bone (2nd ed.). Switzerland: Springer Nature. pp. 257–259. ISBN 978-3-030-28314-8. Archived from the original on 2021-08-31. Retrieved 2021-08-31.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sharif, Ban; Lindsay, Daniel; Saifuddin, Asif (24 July 2021). "Update on the imaging features of the enchondromatosis syndromes". Skeletal Radiology. doi:10.1007/s00256-021-03870-0. ISSN 1432-2161. PMID 34302201. Archived from the original on 31 August 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Suster, David; Hung, Yin Pun; Nielsen, G. Petur (1 January 2020). "Differential Diagnosis of Cartilaginous Lesions of Bone". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 144 (1): 71–82. doi:10.5858/arpa.2019-0441-RA. ISSN 0003-9985. Archived from the original on 19 July 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |