Calcific tendinitis
| Calcific tendinitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: calcified/calcareous tendinitis/tendinopathy, tendinosis calcarea, hydroxyapatite deposition disease, calcific periarthritis | |
 | |
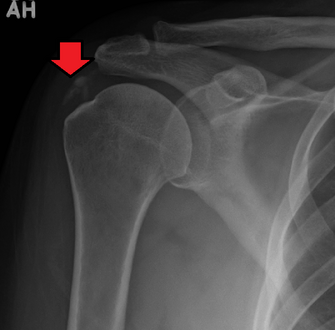
| A plain X ray of the shoulder showing calcific tendinitis | |
| Symptoms | Chronic shoulder pain during activities; acute shoulder pain |
| Duration | Self-limiting, typically resolves in 6-9 months |
| Risk factors | Diabetes, hypothyroidism |
| Diagnostic method | X-ray |
| Treatment | Physiotherapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, surgical excision |
| Medication | NSAIDs |
Calcific tendinitis is a common condition where calcium deposits form in a tendon, sometimes causing pain at the affected site. Deposits can occur in several places in the body, but are by far most common in the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Around 80% of those with deposits experience symptoms, typically chronic pain during certain shoulder movements, or sharp acute pain that worsens at night. Calcific tendinitis is typically diagnosed by physical exam and X-ray imaging. The disease often resolves completely on its own, but is typically treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, rest and physical therapy to promote healing, and in some cases various procedures to breakdown and/or remove the calcium deposits.
Adults aged 30–50 are most commonly affected by calcific tendinitis. It is twice as common in women as men, and is not associated with exercise. Calcifications in the rotator cuff were first described by Ernest Codman in 1934. The name, "calcifying tendinitis" was coined by Henry Plenk in 1952.
Signs and symptoms
Up to 20% of those with calcific tendinitis have no symptoms.[1] For those with symptoms, the symptoms vary based on the phase of the disease. In the initial "formative phase" when the calcium deposits are being formed, people rarely experience any symptoms.[1] Those that do have symptoms tend to have intermittent shoulder pain, particularly during forward should flexion (i.e. lifting the arm in front of the body).[1] In the "resorptive phase" when the calcium deposit is breaking down, many experience severe acute pain that worsens at night.[1] Those affected tend to hold the shoulder rotated inwards to alleviate pain, and have difficulty lying on the affected shoulder.[1] Some people experience heat and redness at the affected shoulder, as well as a limited range of motion.[1]
Cause
Calcific tendinitis is caused by deposits of calcium phosphate crystals in the tendons of the shoulder.[1] These deposits are most frequently found in the supraspinatus tendon (63% of the time), and less frequently in the infraspinatus tendon (7%), subacromial bursa (7%), subscapularis tendon (3%), or in both the supraspinatus and subscapularis tendons at the same time (20%).[1]
The development of calcific tendinitis is often divided into three stages. First, in the "precalcific stage", something causes tendon cells to transform into other cells that can act as sites for calcium deposition.[2] This is followed by the two-part "calcific stage"; first calcium is deposited (the formative phase), then the body begins to break down the calcium deposit (the resporptive phase).[2] Finally, in the "postcalcific stage" the calcium deposits are replaced with new tissue and the tendon completely heals.[2]
The cause of the calcium deposits remains unclear, although several theories have been put forward.[2] Some theories involve the differentiation of tendon cells into other cells, namely cartilages or bone cells.[2] Others associate the condition with cell death due to aging, wear, or lack of oxygen in the tissue; however, the disease is uncommon in the very old, not associated with exercise, and tends to resolve completely even if untreated.[2]
Diagnosis
Calcific tendinitis is typically diagnosed by physical examination and X-ray imaging.[1] During the formative phase, X-ray images typically reveal calcium deposits with uniform density and a clear margin.[1] In the more painful resorptive phase, deposits instead appear cloudy and with unclear margins.[1] By arthroscopy, formative stage deposits appear crystalline and chalk-like, while resorptive stage deposits appear smooth resembling toothpaste.[1] Ultrasound is also used to locate and assess calcium deposits. In the formative stage, deposits are hyperechoic and arc-shaped; in the resorptive stage deposits are less echogenic and appear fragmented.[1][3]
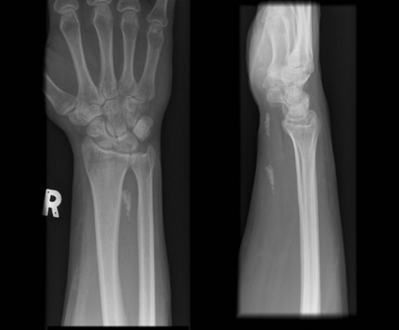
-
Radiographs of wrist demonstrating Calcific tendonitis of flexor carpi ulnaris.
-
An x-ray showing calcific deposits in the area of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles
Treatment
The first line of treatment for calcific tendinitis is typically nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain, rest for the affected joint, and sometimes physical therapy to avoid joint stiffness.[3][1] For those with severe pain direct injections of steroids to the affected site are often effective for pain relief,[1] but may interfere with reabsorption of the calcium deposit.[3] For those whose pain doesn't improve with medication and rest, the deposit can be dissolved and removed with techniques called "ultrasound-guided needling", "barbotage", and "US-PICT" (for "ultrasound percutaneous injection in calcific tenditis"). In each, ultrasound is used to locate the deposit and guide a needle to the affected site. There saline and lidocaine are injected to dissolve the deposit, then removed to wash it away.[1][3][2] Another common treatment is extracorporeal shockwave therapy, where pulses of sound are used to break up the deposit and promote healing.[1] There is little standardization of energy levels, duration, and time interval of treatment; though most studies report positive outcomes with low- to medium-energy waves (below 0.28 mJ/mm2).[3]
Surgery
Surgery is only recommended once 6 months of conservative, non-operative treatment has failed to reduce symptoms. Surgery is arthroscopic and involves calcification removal with or without acromioplasty of the shoulder.[4] Additionally, debate remains over whether a complete removal of the deposits is necessary, or if equal pain relief can be obtained from a partial removal of calcium deposits.[5]
Removing the deposits either with open shoulder surgery or arthroscopic surgery are both difficult operations, but with high success rates (around 90%). About 10% require re-operation. If the deposit is large, then frequently the patient will require a rotator cuff repair to fix the defect left in the tendon when the deposit is removed or to reattach the tendon to the bone if the deposit was at the tendon insertion into the bone.
Outcomes
Nearly all people with calcific tendinitis recover completely with time or treatment.[6] Treatment helps alleviate pain, but long-term follow-up studies have shown that people recover with or without treatment.[6]
Epidemiology
Calcific tendinitis typically occurs in adults aged 30 to 50, and is rare in those older than 70. It is twice as common in women as men.[1]
Risk factors that increase the chance of developing calcific tendinitis include; hormonal disorders, like diabetes and hypothyroidism, autoimmune disorders, like rheumatoid arthritis, and metabolic disorders that also cause kidney stones, gallstones, and gout. Occupations that consist of repetitive overhead lifting, such as athletes or construction workers, do not seem to significantly increase the likelihood of developing calcific tendinitis.[5]
History
Calcifications in the rotator cuff tendon were first described by Ernest Codman in his 1934 book The Shoulder.[3] In 1952, in his study on x-ray therapy for people with such calcifications, Henry Plenk coined the term "calcifying tendinitis".[3][7]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 Kim MS, Kim IW, Lee S, Shin SJ (December 2020). "Diagnosis and treatment of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder". Clin Shoulder Elb. 23 (4): 210–216. doi:10.5397/cise.2020.00318. PMC 7726362. PMID 33330261.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Chianca V, Albano D, Messina C, Midiri F, Mauri G, Aliprandi A, Catapano M, Pescatori LC, Monaco CG, Gitto S, Pisani Mainini A, Corazza A, Rapisarda S, Pozzi G, Barile A, Masciocchi C, Sconfienza LM (January 2018). "Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy: from diagnosis to treatment". Acta Biomed. 89 (1–S): 186–196. doi:10.23750/abm.v89i1-S.7022. PMC 6179075. PMID 29350647.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Merolla G, Singh S, Paladini P, Porcellini G (March 2016). "Calcific tendinitis of the rotator cuff: state of the art in diagnosis and treatment". J Orthop Traumatol. 17 (1): 7–14. doi:10.1007/s10195-015-0367-6. PMC 4805635. PMID 26163832.
- ↑ (2020). .In: Achar, Suraj A. & Taylor, Kenneth S. (eds.), 5-Minute Sports Medicine Consult, The. 3rd Edition. Two Commerce Square, 2001 Market Street, Philadelphia, PA 19103 USA:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Retrieved from: Books@Ovid database.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bechay, Joseph; Lawrence, Cassandra; Namdari, Surena (2020-01-01). "Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff: a review of operative versus nonoperative management". The Physician and Sportsmedicine. 48 (3): 241–246. doi:10.1080/00913847.2019.1710617. ISSN 0091-3847. PMID 31893972. S2CID 209539198.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Miller RH, Azar FM, Throckmorton TW (2021). "Chapter 46: Shoulder and Elbow Injuries". In Azar FM, Beaty JH (eds.). Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. Elsevier. pp. 2374–2425. ISBN 978-0-323-67217-7.
- ↑ PLENK HP (September 1952). "Calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder; a critical study of the value of x-ray therapy". Radiology. 59 (3): 384–9. doi:10.1148/59.3.384. PMID 14958017.
External links
- eMedicine on Calcific Tendonitis Archived 2008-10-30 at the Wayback Machine
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (subscription required) Archived 2007-03-10 at the Wayback Machine
| Classification |
|---|