Baller–Gerold syndrome
| Baller–Gerold syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Craniosynostosis-radial aplasia syndrome[1], Craniosynostosis with radial defects | |
 | |
| The inheritance pattern of Baller-Gerold Syndrome | |
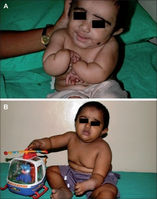
Baller–Gerold syndrome (BGS) is a rare genetic syndrome that involves premature fusion of the skull bones and malformations of facial, forearm and hand bones.[2] The symptoms of Baller–Gerold syndrome overlap with features of a few other genetics disorders: Rothmund–Thomson syndrome and RAPADILINO syndrome.[2] The prevalence of BGS is unknown, as there have only been a few reported cases, but it is estimated to be less than 1 in a million.[2] The name of the syndrome comes from the researchers Baller and Gerold who discovered the first three cases.[3]
Signs and symptoms
The most common and defining features of BGS are craniosynostosis and radial ray deficiency.[4] The observations of these features allow for a diagnosis of BGS to be made, as these symptoms characterize the syndrome.[5] Craniosynostosis involves the pre-mature fusion of bones in the skull.[2] The coronal craniosynostosis that is commonly seen in patients with BGS results in the fusion of the skull along the coronal suture.[6] Because of the changes in how the bones of the skull are connected together, people with BGS will have an abnormally shaped head, known as brachycephaly.[2] Features commonly seen in those with coronal craniosynostosis are bulging eyes, shallow eye pockets, and a prominent forehead.[6] Radial ray deficiency is another clinical characteristic of those with BGS, and results in the under-development (hypoplasia) or the absence (aplasia) of the bones in the arms and the hands. These bones include the radius, the carpal bones associated with the radius and the thumb.[2][7] Oligodactyly can also result from radial ray deficiency, meaning that someone with BGS may have fewer than five fingers.[6] Radial ray deficiency that is associated with syndromes (such as BGS) occurs bi-laterally, affecting both arms.[7]
Some of the other clinical characteristics sometimes associated with this disorder are growth retardation and poikiloderma.[6] Although the presentation of BGS may differ between individuals, these characteristics are often observed. People with BGS may have stunted growth, short stature and misshapen kneecaps.[2] Poikiloderma may also be present in people with this syndrome, meaning that their skin may have regions of hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation, or regions where the skin is missing (atrophy).[8]
-
a) Radical club hand b) after surgery
-
The Coronal suture
Genetics

Baller–Gerold syndrome is caused by a mutation in the RECQL4 gene found on chromosome 8p24.[3] Molecular genetic tests used to identify mutations in the RECQL4 gene include targeted variant analysis and sequence analysis of the entire coding region of the gene.[5] These methods look for changes in the sequence encoding RECQL4, as having a deleterious mutation in the gene will change the protein and disrupt its usual function.[2] RECQL4 is a gene that encodes a DNA helicase in the RecQ helicase family.[10] Helicases are involved with unwinding DNA in preparation for DNA replication and repair.[citation needed]
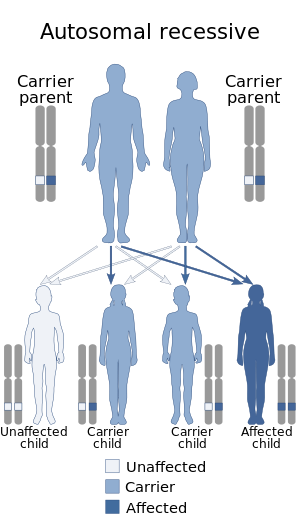
Baller–Gerold syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, meaning that an affected child gets one mutant allele from each parent to produce the syndrome.[3] A carrier is someone who has one mutant allele but does not does have any symptoms. If both parents are carriers, there is a 25% chance the child will have BGS. There is also a 50% chance the child will have one mutant copy (be a carrier) and be asymptomatic and a 25% chance the child will be asymptomatic and not a carrier. In order for someone to have BGS, they need to have two mutant copies of the gene. Adults may pursue genetic counselling to understand the syndrome, as well as the risks and choices regarding family planning.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition is based on the following to ascertain if it is Baller–Gerold syndrome:[11]
- Clinical examination
- Genetic testing.
Treatment
While there is no cure for BGS, symptoms can be treated as they arise. Surgery shortly after birth can repair craniosynostosis, as well as defects in the hand to create a functional grasp.[2] There are risks associated with untreated craniosynostosis, therefore surgery is often needed to separate and reshape the bones.[12] Since patients with a RECQL4 mutation may be at an increased risk of developing cancer, surveillance is recommended.[2][13]
References
- ↑ "Baller-Gerold syndrome (Concept Id: C0265308) - MedGen - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2023-07-05. Retrieved 2024-03-11.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 "Baller-Gerold syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. 2015-11-02. Archived from the original on 2015-12-09. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "OMIM Entry - # 218600 - BALLER-GEROLD SYNDROME; BGS". www.omim.org. Archived from the original on 2021-08-27. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- ↑ Mundlos, Stefan; Horn, Denise (2014-01-01). Baller–Gerold Syndrome. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 205–206. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-95928-1_80. ISBN 978-3-540-95927-4.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Baller-Gerold syndrome - Conditions - GTR - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2015-07-27. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Van Maldergem, Lionel (1993-01-01). Pagon, Roberta A.; Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Wallace, Stephanie E.; Amemiya, Anne; Bean, Lora J.H.; Bird, Thomas D.; Fong, Chin-To; Mefford, Heather C. (eds.). Baller-Gerold Syndrome. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301383. Archived from the original on 2021-08-27. Retrieved 2021-01-12.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Castriota-Scanderbeg, Alessandro; Dallapiccola, Bruno (2006-03-20). Abnormal Skeletal Phenotypes: From Simple Signs to Complex Diagnoses. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540303619. Archived from the original on 2017-02-17. Retrieved 2021-01-12.
- ↑ Schwartz, Robert A. (2012-12-06). Skin Cancer: Recognition and Management. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9781461237907. Archived from the original on 2016-06-17. Retrieved 2021-01-12.
- ↑ Larizza, Lidia; Roversi, Gaia; Volpi, Ludovica (29 January 2010). "Rothmund-Thomson syndrome". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 5 (1): 2. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-5-2. ISSN 1750-1172.
- ↑ "RECQL4 RecQ helicase-like 4 - Gene - GTR - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2021-04-20. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- ↑ "Baller-Gerold syndrome | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 18 March 2021. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ↑ Governale, Lance S. (2015-11-01). "Craniosynostosis". Pediatric Neurology. 53 (5): 394–401. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2015.07.006. PMID 26371995.
- ↑ Lu, Linchao; Jin, Weidong; Liu, Hao; Wang, Lisa L. (2014-01-01). M.D, Eugenie S. Kleinerman (ed.). RECQ DNA Helicases and Osteosarcoma. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 804. Springer International Publishing. pp. 129–145. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-04843-7_7. ISBN 978-3-319-04842-0. PMID 24924172.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |