Asboe-Hansen sign
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Asboe-Hansen sign | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Nikolsky II | |
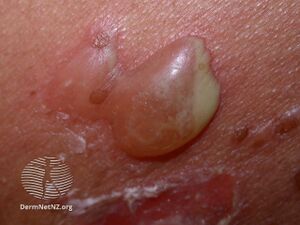 | |
| Pemphigus vulgaris blister | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Causes | Pemphigus vulgaris, severe bullous drug reactions[1] |
The Asboe-Hansen sign refers to the extension of a blister to adjacent unblistered skin when pressure is put on top of it.[2] It is seen along with Nikolsky's sign, both used to assess the severity of some blistering diseases such as pemphigus vulgaris and severe bullous drug reactions.[1]
It is negative in Hailey–Hailey disease and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome.[3]
This sign is named for the Danish physician Gustav Asboe-Hansen (1917–1989), who first described it in 1960.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "2. Cutaneous signs and diagnosis". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2023-02-09. Retrieved 2023-06-21.
- ↑ Jonkman, Marcel F.; Horváth, Barbara (2022). "2. Dermatological examination of bullous diseases". In Horváth, Barbara (ed.). Autoimmune Bullous Diseases (2nd ed.). Switzerland: Springer. pp. 11–28. ISBN 978-3-030-91557-5. Archived from the original on 2023-06-30. Retrieved 2023-06-21.
- ↑ Diwaan, Nikkhiel; Sapkal, Rashmi; Kureel, Kamana; Pathan, Sabah; Mujawar, Aadia; Supnekar, Shraddha; Patel, Husna (April 2020). "Exploring Nikolsky's Sign" (PDF). IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences. 19 (4). doi:10.9790/0853-1904090103. ISSN 2279-0853. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-04-18. Retrieved 2022-04-18.
- ↑ Freiman, Anatoli; Kalia, Sunil; O'Brien, Elizabeth A. (July 2006). "Dermatologic Signs". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 10 (4): 175–182. doi:10.2310/7750.2006.00042.
- ↑ Ganapati, Sentamilselvi (2014). "Eponymous Dermatological Signs in Bullous Dermatoses". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 59 (1): 21–23. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.123483. ISSN 0019-5154. PMID 24470655. Archived from the original on 2022-04-18. Retrieved 2022-04-17.