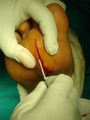
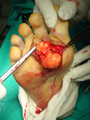
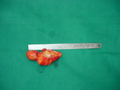
Angiolipoma
| Angiolipoma | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Other specified lipoma[1] | |
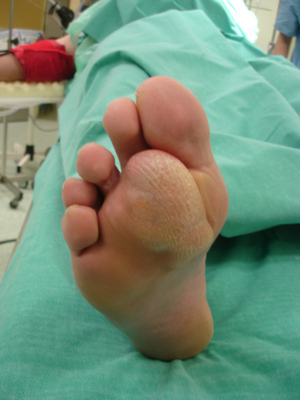 | |
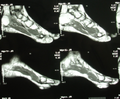
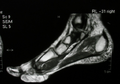
| Angiolipoma foot | |
| Symptoms | Multiple tender lumps just under the skin[1] |
| Usual onset | Second/third decade of life[1] |
| Causes | Unknown[1] |
| Prognosis | Good, typically do not recur[1] |
| Frequency | Common[1] |
Angiolipoma is a non-cancerous soft tissue tumor.[1] It generally presents as multiple tender lumps just under the skin, most frequently affecting the limbs and less commonly the trunk.[1]
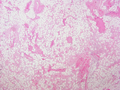
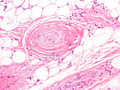
The cause is unknown.[1] It has all other features of a typical lipoma.[2]: 624 [3] When surgically removed, it appears yellow-red with a capsule.[1] Under the microscope, it features mature adipocytes and branching vessels of capillary size, which typically contain fibrin thrombi.[1]
Males are affected more frequently than females.[1] Around 5% of cases run in families in an autosomal dominant manner.[1]
Signs and symptoms
-
Large mediastinal angiolipoma
Pathology
-
Small vessels in adipose tissue
-
Small vessels in adipose tissue
-
Small vessels in adipose tissue
-
Small vessels in adipose tissue
-
The vessels typically contain hyaline or fibrin (pictured) thrombi[4]
-
-
-
Diagnosis
It may appear similar to Kaposi sarcoma and angiosarcoma.[1]
Treatment
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, ed. (2020). "1. Soft tissue tumours: Angiolipoma". Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours. Vol. 3 (5th ed.). Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer. pp. 23–24. ISBN 978-92-832-4503-2.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1838. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ↑ Vijay Shankar. "Soft tissue - Adipose tissue tumors - Lipoma and variants - Angiolipoma". Pathology Outlines. Archived from the original on 2020-10-24. Retrieved 2021-01-07. Topic Completed: 1 August 2012. Minor changes: 20 March 2019
External links
| Classification |
|
|---|





![The vessels typically contain hyaline or fibrin (pictured) thrombi[4]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/44/Histopathology_of_angiolipoma.jpg/120px-Histopathology_of_angiolipoma.jpg)