Aneurysmal bone cyst
| Aneurysmal bone cyst | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Not recommended: Giant cell reparative granuloma of small bone, giant cell lesion of small bones[1] | |
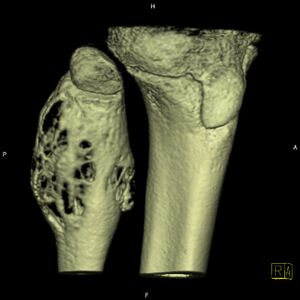 | |
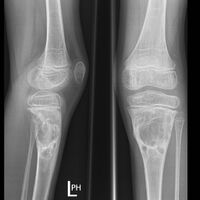
| Aneurysmal bone cyst (fibula, around knee). | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics[1] |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, pressure related neurological symptoms[1] |
| Causes | Unknown[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging. CT scan and X-ray: lytic expansion lesion its clear border. MRI: fluid levels. Bone scan: peripheral radiotracer uptake, with a central Photopenic area.[1] |
| Differential diagnosis | Telangiectatic osteosarcoma[1] |
| Treatment | Surgery[2] |
| Prognosis | 20-70% recur after curettage.[1] |
| Frequency | Rare,[3] ~0.15 cases per one million per year.[1] 80% age <20 years.[1] M=F[1] |
Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC), is a non-cancerous bone tumor comprised of multiple varying sizes of spaces in a bone which are filled with blood.[1][4] The term is a misnomer, as the lesion is neither an aneurysm nor a cyst.[5] It generally presents with pain and swelling in the affected bone.[1] Pressure on neighbouring tissues may cause compression effects such as neurological symptoms.[1]
The cause is unknown.[1] Diagnosis involves medical imaging.[1] CT scan and X-ray show lytic expansion lesions with clear borders.[1] MRI reveals fluid levels.[1]
Treatment is usually by curettage, bone grafting or surgically removing the part of bone.[2] 20-30% may recur, usually in the first couple of years after treatment, particularly in children.[2]
It is rare.[3] The incidence is around 0.15 cases per one million per year.[1] Aneurysmal bone cyst was first described by Jaffe and Lichtenstein in 1942.[5][6]
Signs and symptoms
It generally presents with pain and swelling in the affected bone in someone under the age of 20.[2] Pressure on neighbouring tissues may cause compression effects such as neurological symptoms.[1]
The afflicted may have relatively small amounts of pain that will quickly increase in severity over a time period of 6–12 weeks. The skin temperature around the bone may increase, a bony swelling may be evident, and movement may be restricted in adjacent joints.[7]
ABC in the spine may cause spinal cord compression.[1]
People with skull lesions may have headaches.[citation needed]
Sites
Commonly affected sites are the spine, thigh bone and lower leg bone.[2] Approximate percentages by sites are as shown:[citation needed]
- Lower leg (24%)
- Upper extremity (21%)
- Spine (16%)
- Pelvis and sacrum (12%)
- Femur (13%)
- Clavicle and ribs (5%)
- Skull and mandible (4%)
- Foot (3%)
Causes
The cause is unknown.[1]
Aneurysmal bone cyst has been widely regarded a reactive process of uncertain cause since its initial description by Jaffe and Lichtenstein in 1942. Many hypotheses have been proposed to explain the cause and pathogenesis of aneurysmal bone cyst, and until very recently the most commonly accepted idea was that aneurysmal bone cyst was the consequence of an increased venous pressure and resultant dilation and rupture of the local vascular network. However, studies by Panoutsakopoulus et al. and Oliveira et al. uncovered the clonal neoplastic nature of aneurysmal bone cyst. Primary cause has been regarded arteriovenous fistula within bone.[8] The lesion may arise de novo or may arise secondarily within a pre-existing bone tumor, because the abnormal bone causes changes in hemodynamics. An aneurysmal bone cyst can arise from a pre-existing chondroblastoma, a chondromyxoid fibroma, an osteoblastoma, a giant cell tumor, or fibrous dysplasia. A giant cell tumor is the most common cause, occurring in 19% to 39% of cases. Less frequently, it results from some malignant tumors, such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and hemangioendothelioma.[citation needed]
Mechanism

Histologically, they are classified in two variants.[citation needed]
- The classic (or standard) form (95%) has blood filled clefts among bony trabeculae. Osteoid tissue is found in stromal matrix.
- The solid form (5%) shows fibroblastic proliferation, osteoid production and degenerated calcifying fibromyxoid elements.
According to Buraczewski and Dabska, the development of the aneurysmal bone cyst follows three stages.[5]
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial phase (I) | Osteolysis without peculiar findings |
| Growth phase (II) |
|
| Stabilization phase (III) | Fully developed radiological pattern |
They can also be associated with a TRE17/USP6 translocation.[9]
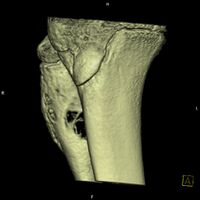
Aneurysmal bone cysts may be intraosseous, staying inside of the bone marrow. Or they may be extraosseous, developing on the surface of the bone, and extending into the marrow. A radiograph will reveal a soap bubble appearance.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Imaging
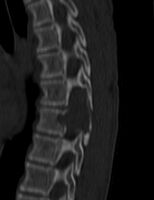
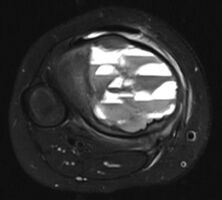
X-ray and CT scan show lytic expansion lesions with clear borders.[1] Expansion of cortex gives the lesion a balloon-like appearance. Larger lesions may appear septated.[10] MRI reveals fluid levels.[1] Bone scan shows outer radiotracer uptake, with a central dark area.[1]
-
X-ray: ABC large long bone of lower leg near knee
-
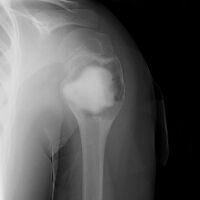
ABC shoulder
-
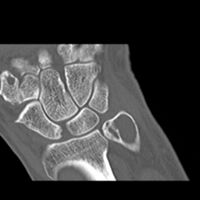
CT scan: ABC ulna near wrist
-
CT scan: ABC fibula
-
CT scan: ABC spine
-
MRI scan: showing fluid levels
-
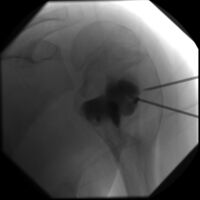
DSA: ABC of shoulder
-
Bone scan: ABC left radius
Histopathology
The wall of the spaces comprises fibroblasts, osteoclast-like giant cells, haemosiderin pigment, and newly forming bone.[1]
-
High magnification micrograph of an ABC
-
Intermediate magnification micrograph of an ABC
Differential diagnosis
The term secondary aneurysmal bone cyst is no longer used.[1]
The main differential diagnosis is telangiectatic osteosarcoma.[1] Others include chondroblastoma, unicameral bone cyst and giant cell tumor.[11]
Treatment
Curettage is performed on some patients,[12] and is sufficient for inactive lesions. The recurrence rate with curettage is significant in active lesions, and marginal resection has been advised. Liquid nitrogen, phenol, methyl methacrylate are considered for use to kill cells at margins of resected cyst.[8]
Outcomes
20-70% recur after curettage.[1]
Epidemiology
It is rare.[3] The incidence is around 0.15 cases per one million per year.[1] 80% occur in people age less than 20 years.[1] It is second most common tumor of spine and most common benign tumor of pelvis in pediatric population.[8] Males are affected as equally as females.[1]
History
Aneurysmal bone cyst was first described by Jaffe and Lichtenstein in 1942.[5][6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.23 1.24 1.25 1.26 1.27 1.28 1.29 1.30 WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, ed. (2020). "3. Bone tumours: simple bone cyst". Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours. Vol. 3 (5th ed.). Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer. pp. 437–439. ISBN 978-92-832-4503-2. Archived from the original on 2021-06-13. Retrieved 2021-06-25.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Bone tumours. What are Bone Tumours?". patient.info. Archived from the original on 24 April 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Muratori, Francesco; Mondanelli, Nicola; Rizzo, Anna Rosa; Beltrami, Giovanni; Giannotti, Stefano; Capanna, Rodolfo; Campanacci, Domenico Andrea (10 November 2019). "Aneurysmal Bone Cyst: A Review of Management". Surgical Technology International. 35: 325–335. ISSN 1090-3941. PMID 31476792. Archived from the original on 25 June 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ↑ Stevens, Kyle J.; Stevens, James A. (5 September 2020). "Aneurysmal Bone Cysts". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Maroldi, Roberto (2005). Imaging in Treatment Planning for Sinonasal Diseases. Springer. pp. 114–116. ISBN 9783540266310. Archived from the original on 2021-06-25. Retrieved 2021-05-02.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Tomasik, Patryk; Spindel, Jerzy; Miszczyk, Leszek; Chrobok, Adam; Koczy, Bogdan; Widuchowski, Jerzy; Mrozek, Tomasz; Matysiakiewicz, Jacek; Pilecki, Bolesław (September 2009). "Treatment and differential diagnosis of aneurysmal bone cyst based on our own experience". Ortopedia, Traumatologia, Rehabilitacja. 11 (5): 467–475. ISSN 1509-3492. Archived from the original on 2021-06-25. Retrieved 2021-06-24.
- ↑ Zadik, Yehuda; Aktaş Alper; Drucker Scott; Nitzan W Dorrit (2012). "Aneurysmal bone cyst of mandibular condyle: A case report and review of the literature". J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 40 (8): e243–8. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2011.10.026. PMID 22118925.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Springer. 2007. pp. 151–155. ISBN 9783540699644.
- ↑ Ye Y, Pringle LM, Lau AW, et al. (June 2010). "TRE17/USP6 oncogene translocated in aneurysmal bone cyst induces matrix metalloproteinase production via activation of NF-kappaB". Oncogene. 29 (25): 3619–29. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.116. PMC 2892027. PMID 20418905.
- ↑ Davies, Arthur (2002). Who Manual Of Diagnostic Imaging: Radiographic Anatomy And Interpretation Of The Muskuloskeletal System, VOlume. World Health Organization. pp. 168–186. ISBN 9241545550.
- ↑ Stevens, Kyle J.; Stevens, James A. (5 September 2020). "Aneurysmal Bone Cysts". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ↑ Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Ortiz-Cruz E, Villafuerte J, Gebhardt MC (September 2005). "Aneurysmal bone cyst: a review of 150 patients". J. Clin. Oncol. 23 (27): 6756–62. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.15.255. PMID 16170183. Archived from the original on 2013-04-15.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |